
If the values do not match, download the file again and repeat this procedure. CMD as admin C:Windowssystem32>CertUtil -hashfile. Another built in way- CertUtility can be used to verify md2,3,4,5 sha1,256,384,512.

$> 3a4a903b80f75618698c6ba66aca0b298ab861f75ae0b2322a661a593cae2a51 ManageEngine_ApplicationsManager_64bit.exe In this example, the file is stored in the folder /CC/Checksum.
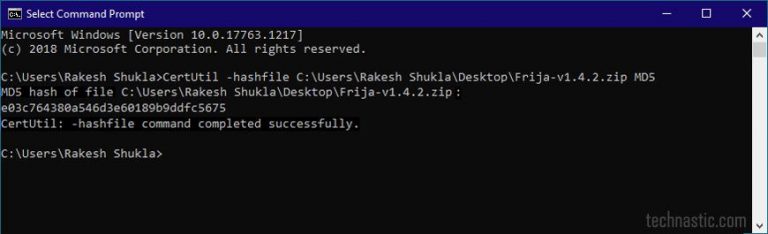
$> shasum -a 256 ManageEngine_ApplicationsManager_64bit.exe $> sha256sum ManageEngine_ApplicationsManager_64bit.bin (The sample output is mentioned below each command)Ĭ:\Users\Downloads> CertUtil -hashfile ManageEngine_ApplicationsManager_64bit.exe SHA256 Based on the OS you are using, execute the command mentioned.If no files are specified, the cksum command reads standard input. The cksum command reads the files specified by the File parameter and calculates a 32-bit checksum Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) and the byte count for each file. Now the ‘MD5’ (or whatever you had called at the p.2 above) option should appear in your right-click > ‘Send to’ menu. Displays the checksum and byte count of a file. Navigate to the directory in which the downloaded file exists. cmd (e.g., MD5.cmd) file with the following content: certutil -hashfile 1 md5.

Open command prompt with administrator privileges.It helps identify if the downloaded file has been corrupted.Īfter you have downloaded Applications Manager binaries, you should ensure that its SHA256 checksum matches the one provided in the Applications Manager download pages.
Windows checksum command verification#
SHA256 checksum verification helps verify integrity of files you download.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
